Can Meerkats Be Pets: Complete Guide to Meerkat Ownership Laws and Care Requirements
Understand meerkats as potential pets
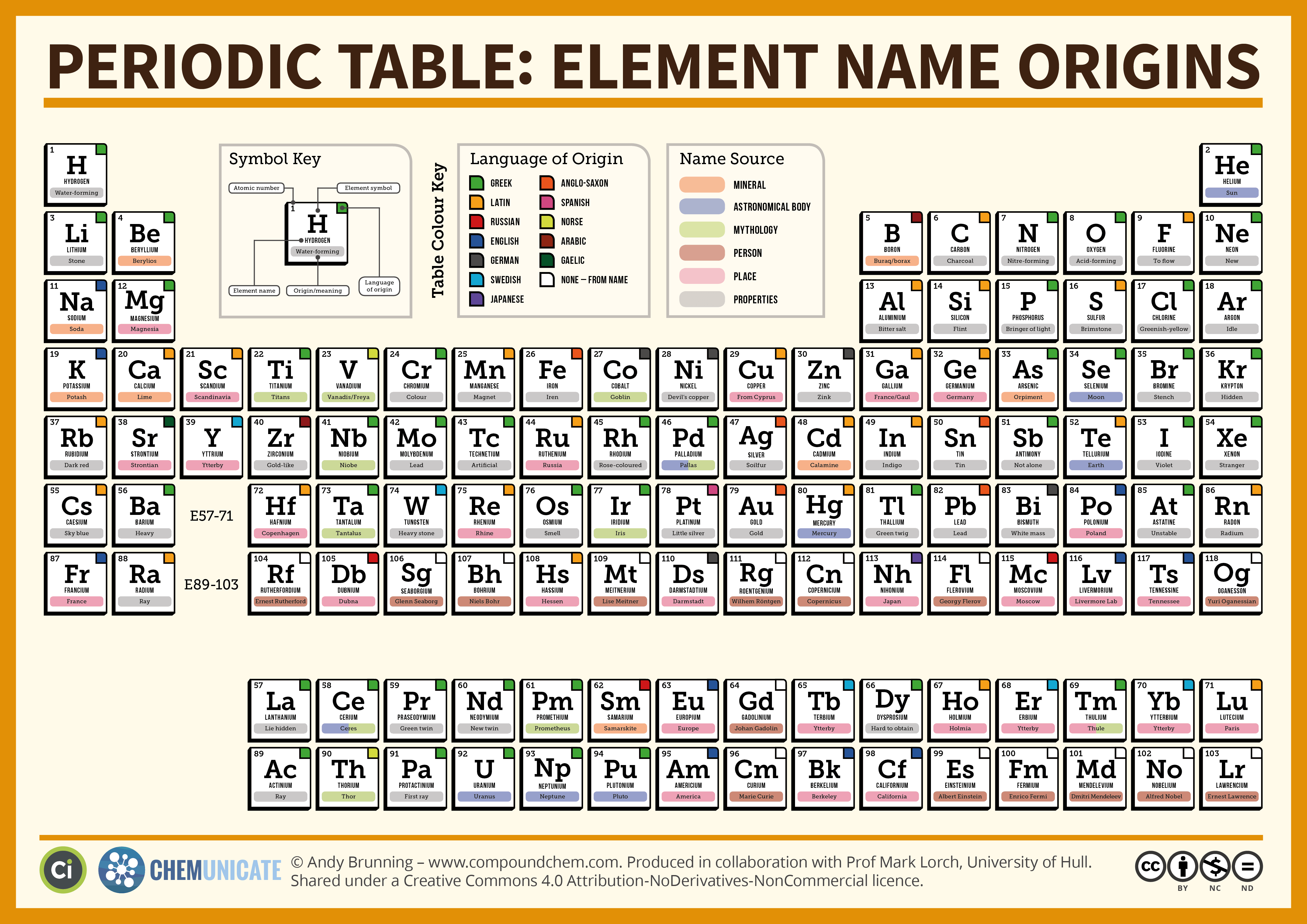
Meerkats captivate people planetary with their upright posture, social behaviors, and expressive faces. These small African mammals belong to the mongoose family and have gain popularity through documentaries and movies. Yet, whether meerkats can be pets involve complex legal, ethical, and practical considerations that potential owners must understand.
The simple answer is that meerkats make exceedingly poor pets and are illegal to own in most jurisdictions. These wild animals have evolved specific behavioral and physical needs that can not be meet in domestic settings. Their complex social structure, specialized diet, and natural instincts make them unsuitable for life as companion animals.
Legal restrictions on meerkat ownership
Most countries and states prohibit private ownership of meerkats. In the United States, federal regulations under the Lacey act restrict the importation and interstate transport of many exotic species, include meerkats. Individual states maintain their own exotic animal laws, with virtually classify meerkats as prohibit species.
The convention on international trade in endangered species of wild fauna and flora (cites )regulate international trade in meerkats. While not presently endanger, meerkats are prprotectednder various wildlife conservation laws in their native range across Southern Africa.
Violate exotic animal ownership laws can result in significant penalties, include hefty fines, criminal charges, and confiscation of the animal. Law enforcement agencies work intimately with wildlife officials to investigate illegal exotic pet ownership.
Natural behavior and social structure
Meerkats are extremely social animals that live in complex family groups call mobs or gangs. These groups typically consist of 10 to 30 individuals with intricate hierarchical structures. Dominant females lead the group, while subordinate members perform specific roles include sentinel duty, forage, and pup care.
Their communication system involve over 30 distinct vocalizations, each serve specific purposes such as alarm calls, contact calls, and social coordination. Meerkats spend most of their day forage unitedly, with designate sentries watch for predators while others search for food.

Source: pethelpful.com
The social bonding in meerkat groups is essential for their psychological well-being. Isolated meerkats experience severe stress and can develop behavioral abnormalities. This fundamental need for complex social interaction can not be replicate in domestic environments.
Specialized dietary requirements
Meerkats are principally insectivores with extremely specialized dietary needs. Their natural diet consist of beetles, caterpillars, spiders, and scorpions, make up roughly 80 % of their food intake. They besides consume small reptiles, birds, eggs, and occasionally plant matter.

Source: pethelpful.com
These animals have evolved to process specific nutrients find in their native prey species. Their digestive systems areadaptedt to handle the chitin in insect exoskeletons and the various toxins find in their prey, include scorpion venom.
Replicate this diet in captivity require extensive knowledge and resources. Commercial exotic animal diets can not amply substitute for their natural food sources. Nutritional deficiencies usually occur in captive meerkats, lead to health problems include metabolic bone disease, dental issues, and immune system dysfunction.
Physical environment and habitat need
Meerkats inhabit the semi arid regions of the Kalahari Desert, where they dig extensive burrow systems. These underground networks can extend several meters deep and contain multiple chambers for sleeping, nurseries, and boltholes for escape from predators.
Temperature regulation is crucial for meerkats. They require access to both warm basking areas and cool underground retreats. Their burrow systems maintain stable temperatures year round, which can not be replicate in typical domestic settings.
The territorial range of a meerkat mob can span several square kilometers. They need extensive space for forage, territorial marking, and natural behaviors. Confinement in small spaces lead to stress relate behaviors include repetitive movements, aggression, and self harm.
Health and veterinary challenges
Meerkats are susceptible to various diseases and health conditions that require specialized veterinary care. Many common veterinarians lack experience treat these exotic species, make proper medical care difficult to obtain.
Zoonotic diseases pose risks to human health. Meerkats can carry tuberculosis, rabies, and various parasites that are transmissible to humans. Their sharp claws and teeth can inflict serious injuries, and their unpredictable nature make handle dangerous.
Stress relate illnesses are common in captive meerkats. These include gastrointestinal disorders, reproductive problems, and behavioral abnormalities. The chronic stress of captivity weaken their immune systems, make them more susceptible to infections and diseases.
Behavioral problems in captivity
Captive meerkats oftentimes develop severe behavioral problems due to their inability to express natural behaviors. These include excessive digging, repetitive pacing, aggression toward humans, and destructive behaviors.
Their natural instinct to dig extensive burrow systems lead to destructive behavior in homes. Meerkats will attempt to dig through floors, walls, and furniture, will cause significant property damage.
The lack of appropriate social structure in captivity can lead to psychological distress. Single meerkats may become excessively attach to human caretakers or develop aggressive tendencies. Yet pairs or small groups can not replicate the complex social dynamics of wild meerkat mobs.
Ethical considerations
The exotic pet trade contributes to the exploitation of wild animal populations. Many meerkats in the pet trade are capture from wild populations, disrupt natural social groups and ecosystems.
Breed programs for the pet trade oftentimes involve poor conditions and inadequate care. The complex social and environmental needs of meerkats can not be meet in commercial breeding facilities focus on profit kinda than animal welfare.
Wildlife conservation organizations powerfully oppose keep meerkats as pets. These animals play important ecological roles in their native habitats, and remove them from wild populations can have negative environmental impacts.
Alternatives for meerkat enthusiasts
People fascinate by meerkats have several alternatives to ownership. Many zoos and wildlife sanctuaries offer educational programs and volunteer opportunities that allow close interaction with these animals in appropriate settings.
Wildlife photography and ecotourism provide opportunities to observe meerkats in their natural habitats. Several reserves in sSouth Africaoffer guide tours where visitors can watch wild meerkat colonies.
Support meerkat conservation efforts through donations and advocacy help protect these animals in their natural environments. Organizations work to preserve meerkat habitats and study their behavior offer ways to contribute to their welfare without keep them as pets.
Domestic alternatives with similar appeal
Pet enthusiasts draw to meerkats might consider domestic animals with similar characteristics. Ferrets share some behavioral traits with meerkats, include social nature and playful personalities, while being lawfully keep as pets in many areas.
Prairie dogs, where legal, exhibit some of the social behaviors that make meerkats appeal. Nonetheless, these animals besides have complex needs and are restricted in many jurisdictions.
For those interested in the upright posture and alert nature of meerkats, certain dog breed like Jack Russell terriers or rat terriers can provide similar visual appeal while being appropriate companion animals.
The reality of exotic pet ownership
The exotic pet industry oftentimes promote unrealistic expectations about wild animal ownership. Marketing materials seldom address the complex needs, legal restrictions, and ethical concerns associate with keep exotic species as pets.
Many exotic animals, include meerkats, are abandon or surrender when owners realize they can not provide appropriate care. Wildlife sanctuaries and rescue facilities are oftentimes overwhelmed with exotic animals that can no farseeing be care for by private owners.
The financial costs of right care for exotic animals far exceed those of traditional pets. Specialized diets, veterinary care, housing modifications, and legal compliance can cost thousands of dollars yearly.
Conclusion
Meerkats can not and should not be keep as pets. These remarkable animals have evolved complex social, behavioral, and environmental needs that can not be meet in domestic settings. Legal restrictions exist for good reasons, protect both the animals and public safety.
The appeal of meerkats is understandable, but responsible animal appreciation involve respect their wild nature and support their conservation in natural habitats. Those interested in these fascinating creatures can find fulfilling ways to learn about and support meerkats without attempt to keep them as pets.
Understand why certain animals make poor pets help promote responsible pet ownership and wildlife conservation. The best way to appreciate meerkats is to support their protection in the wild, where they can live accord to their natural behaviors and contribute to healthy ecosystems.
MORE FROM lowcostbotox.com