How Digital Technology Empowers Everyone to Create Multimedia Content
Introduction: The New Age of Multimedia Creation
In the past, producing multimedia content-combining images, video, audio, and interactive elements-required specialized skills and expensive equipment. Today, digital technology has democratized multimedia creation , enabling anyone with a computer or smartphone to craft compelling digital experiences. This radical accessibility opens doors for individuals, small businesses, educators, and communities to communicate, educate, and entertain without traditional barriers. This article explains how digital technology makes this possible, provides actionable guidance, and highlights inclusive practices so your content reaches the broadest possible audience.
Accessible Devices and Software: Removing Barriers to Entry
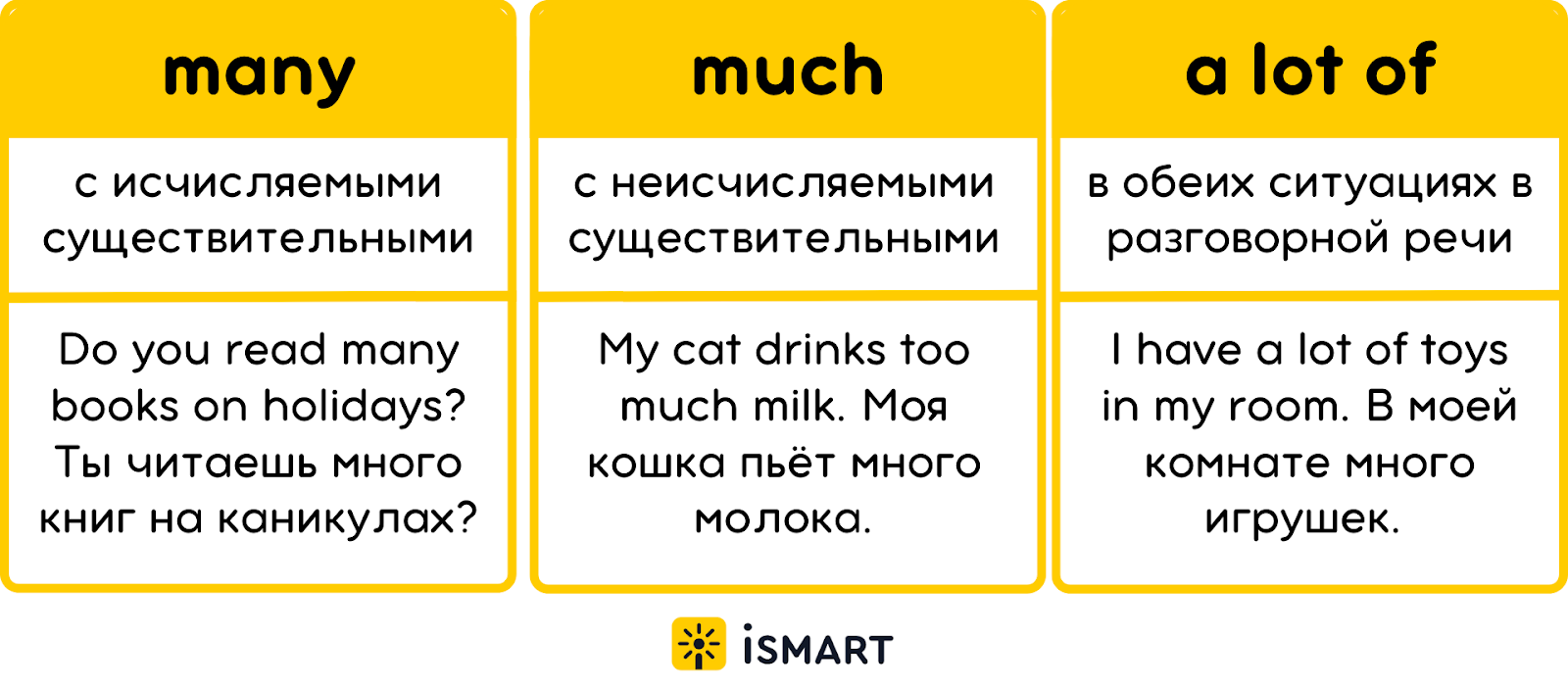
One of the most significant changes brought by digital technology is the availability of affordable and user-friendly devices and software . Smartphones, tablets, and modern computers come equipped with integrated cameras, microphones, and editing tools, allowing users to capture and edit multimedia content directly on their device. Free and low-cost applications such as video editors, graphic design tools, and audio recorders are widely available through official app stores or pre-installed on many devices.
For example, most smartphones now ship with built-in video editing apps, while platforms like Canva and Audacity offer intuitive interfaces for graphic design and audio editing, respectively. These tools are designed with accessibility and ease-of-use in mind, often including drag-and-drop functionality and guided templates, so even beginners can produce professional-looking content.
To get started, you can:
- Explore the app store on your device for multimedia editing tools (e.g., search for “video editor” or “audio recorder” on your phone).
- Try cloud-based platforms like Canva for design or Soundtrap for collaborative audio projects. Search for these services using their brand names to ensure you access the official websites.
Inclusive Design and Digital Accessibility: Creating for Everyone
Digital technology not only simplifies creation but also emphasizes accessibility and inclusivity . Accessible digital content ensures that everyone, including people with disabilities, can perceive, navigate, and interact with your work [1] . This includes adding alt text to images, providing captions for videos, and ensuring keyboard navigation for web-based content [2] .
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) offer a framework for making content operable, perceivable, robust, and understandable. For instance, including descriptive alt text allows screen readers to convey image information to visually impaired users, while closed captions make video content accessible to those who are deaf or hard of hearing [3] .
To create accessible multimedia content:
- Add alternative text descriptions to all images.
- Include captions or transcripts for audio and video content.
- Use high-contrast color schemes and readable fonts.
- Structure documents and web pages with clear headings and logical order.
Many software platforms now include built-in accessibility checkers to help identify and address potential barriers before publishing your content.
Assistive Technology and Supportive Coding Practices
Assistive technologies-such as screen readers, voice recognition software, and alternative input devices-enable individuals with disabilities to interact with digital content. Digital technology supports these tools through proper coding and semantic structure . For websites and apps, using semantic HTML and ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) labels ensures that assistive devices can interpret and navigate content accurately [5] .
For example, ensuring your website’s navigation can be tabbed through with a keyboard, rather than requiring a mouse, allows individuals with limited mobility to access all features. ARIA labels can clarify the purpose of buttons, forms, or menus for screen reader users, further enhancing inclusivity.
Steps to enhance assistive technology compatibility include:
- Structure content with headings, lists, and tables using semantic code.
- Apply ARIA labels to interactive elements such as buttons and navigation menus.
- Test your content with screen reader software or accessibility checkers available in most content management systems (CMS).
If you’re unsure how to implement these features, consider searching for “web accessibility best practices” or contacting disability advocacy organizations for guidance.
Cloud Platforms and Collaboration: Working Together from Anywhere
Cloud-based platforms allow individuals and teams to collaborate on multimedia projects regardless of location . Services like Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, and Adobe Creative Cloud offer shared documents, real-time editing, and multimedia integration. These platforms often include accessibility features, such as real-time captions in video calls or accessibility checker tools for documents [4] .
To leverage cloud platforms for multimedia creation:
- Sign up for cloud-based productivity suites using your official email address.
- Explore built-in accessibility and collaboration features, such as shared editing or live captions.
- Read official help guides or search for “cloud collaboration for multimedia” for tips and tutorials.
These collaborative tools are especially valuable for remote teams, educators, and community groups seeking to produce and share content efficiently.
Legal and Ethical Considerations: Meeting Standards and Fostering Inclusion
In the United States and many other countries, there are legal requirements for digital accessibility . Laws such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act mandate that digital content be accessible to people with disabilities [3] . Failing to comply can result in legal action and exclusion of significant audiences.
To ensure compliance:
- Familiarize yourself with relevant accessibility standards (e.g., WCAG, ADA, Section 508).
- Consult official resources or seek expert advice if your content targets broad or public audiences.
- Regularly update your knowledge, as legal requirements and best practices evolve.
By prioritizing accessibility, you not only avoid legal risks but also demonstrate a commitment to inclusive communication and social responsibility.

Source: youtube.com
Getting Started: Step-by-Step Guidance for Aspiring Creators
If you are new to multimedia creation, follow these steps to get started:
- Define Your Goals: Decide what type of multimedia content you want to create (e.g., video, podcast, interactive website).
- Choose Your Tools: Identify accessible software or platforms suited to your project. Use official app stores or search for reputable brands and check for accessibility features.
- Plan for Accessibility: Design your content with accessibility from the start. Use templates or guides that comply with WCAG and ADA requirements.
- Create and Edit: Capture your media using your device, then edit using your chosen software. Add accessibility features like alt text, captions, and logical structure.
- Test and Review: Use built-in accessibility checkers, screen readers, or seek feedback from individuals with disabilities to ensure your content is inclusive.
- Publish and Share: Share your content on accessible platforms and invite feedback to further improve your approach.
If you need help, consider searching for digital accessibility training from trusted organizations or reaching out to local libraries and community centers for workshops.
Alternative Approaches and Overcoming Challenges
While technology has lowered barriers, some users may still face challenges, such as lack of access to high-speed internet or up-to-date devices. Solutions include:

Source: es.learniv.com
- Accessing public resources like libraries or community centers that offer free internet and devices.
- Searching for local non-profits or government programs that provide digital literacy training or device loans.
- Joining online forums and communities for peer support and advice on accessible multimedia creation.
For more advanced needs, consider collaborating with accessibility consultants or seeking out organizations specializing in digital inclusion.
Key Takeaways
- Digital technology has made multimedia creation accessible for nearly everyone.
- Emphasizing accessibility and inclusive design expands your audience and meets legal requirements.
- Numerous free and affordable tools are available for every stage of the multimedia creation process.
- Cloud platforms and assistive technologies further support collaboration and access for all.
Whether you are an individual creator or part of a larger organization, embracing these practices ensures your digital content is engaging, inclusive, and effective.
References
- [1] HandTalk (2023). Accessible digital content: how to create it and why it matters.
- [2] AbilityNet (2023). 10 FAQs about creating accessible digital content.
- [3] UF Health (2023). What Is Digital Accessibility?: Best Practices and Guidelines.
- [4] Georgetown University (2023). Digital Accessibility.
- [5] Level Access (2024). Assistive Technology in Digital Inclusion | Types & examples.
MORE FROM lowcostbotox.com